
However, there is no evidence that a specific foot structure or dynamic foot behavior during loading means an increased risk of injury ( Buldt et al., 2013).
#Pes cavus Pc#
Finding typical foot structures validated to the dynamic behaviour during running could provide the clinician with a valuable and quick assessment tool to separate abnormal structures (referring to PC and PP) and predispose abnormal biomechanics (referring to hyperpronation and hypersupination) in order to plan a suitable treatment. Meanwhile sports medicine literature has blamed excessive pronation as the cause for nearly all maladies of the lower extremities, further supported in other studies ( Dahle et al., 1991 Kannus, 1992). (1999) presented an increased risk of injuries in high- and low-arched runners compared to those with normal arches. Lack of consistency in previous research and difficulties in comparing the results of the studies due to the use of various measurement methods have been suggested as reasons ( Williams and McClay, 2000). However, neither a characteristic mobility nor a characterized biomechanical compensation pattern under load (referring to the excessive or nonexcessive supination or pronation) of a PC and PP has previously been established. Pes Rectus rarely develops excessive compensatory movement patterns. Based on this theory, Pes Planus (PP) is often described as being more mobile and developing into hyperpronation, while Pes Cavus (PC) is more rigid and develops into hypersupination. A previous study reported that the structure of the Medial Longitudinal Arch (MLA) and the position of the subtalar joint (STJ) axes affect each other independently, were the MLA is lowered through the STJ eversion and vice versa ( Subotnick, 1974). In clinical practice, it is common to use the foot structure as a predictor of its behavior under load. Keywords: Calcaneus deviation, Fatigue, Foot, Pronation, Subtalar joint, Supination

The effect of fatigue evident in the present study suggests that further biomechanical research should be considered when exposing the foot to the repetitive nature of running, conditions most likely responsible for the overrepresented overuse injuries among runners.

Between the groups, there was a significantly greater eversion of the Pes Planus, on the right foot, after 45 min of running ( P<0.05) compared to the Pes Cavus. Both individuals with Pes Cavus and Pes Planus showed a significant increase in the calcaneal eversion ( P<0.05) after 45 min of running.
#Pes cavus software#
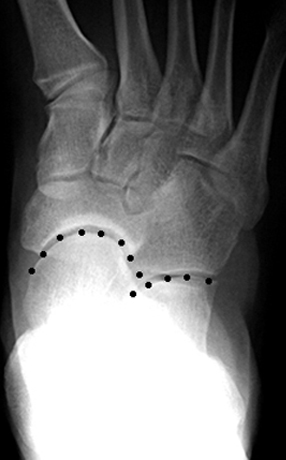
The calcaneal vertical angle, representing the eversion/inversion of the subtalar joint, was measured using with two-dimensional digital analysis and Dartfish Software with the subjects running barefoot on a treadmill, before and after 45 min of outside running wearing shoes. Thirty-four subjects, meeting the requirements for Pes Planus (30 feet) and Pes Cavus (35 feet), according to the criteria for Medial Longitudinal Arch-angle, were included in the study. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the possible differences in the subtalar joint in the midstance phase of running, between individuals with Pes Planus and Pes Cavus, after 5 min and 45 min of running. In sports, there is a constant discussion about the hyper-pronation and supination of the foot during loading and its relation to injuries or discomfort.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
